Giant Cell Bone Tumors: Definition and Treatment Methods
1. Introduction
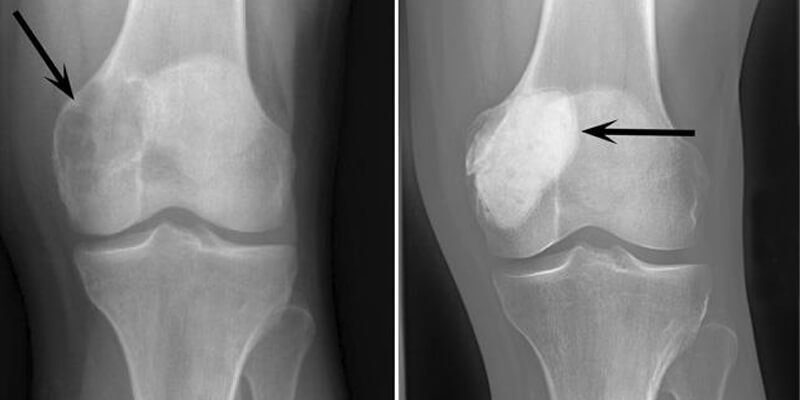
Giant cell bone tumors are rare but aggressive tumors that grow in bone tissue. These types of tumors usually occur in the limbs, especially in large bones such as the knee or arm. Although they are usually seen in young adults and teenagers, they can occur at any age. This article aims to cover the definition and treatment methods of giant cell bone tumors in detail. It aims to guide patients in the diagnosis and treatment of such tumors.
2. Definition of Giant Cell Bone Tumors
Giant cell bone tumors are a rare type of tumor that occurs in bone tissue. They are usually seen in long bones, especially the kneecap, upper arm or upper leg bones. In these types of tumors, the cells grow and spread rapidly. They are generally considered aggressive and can be difficult to treat. Symptoms of such tumors include:
- Pain
- Swelling
- Bone fragility
- Limited movement
Diagnosis is usually made using methods such as X-ray, MRI, and biopsy. Giant cell bone tumors can have a better prognosis with early diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
3. Epidemiology and Risk Factors
Giant cell bone tumors are a rare type of tumor that is usually seen in young adults. According to epidemiological data, the incidence of such tumors is increasing every year. Risk factors include:
- Genetic predisposition
- Radiation exposure
- Certain gene mutations
However, determining a definitive risk factor is a difficult process and research is ongoing.
4. Clinical Findings and Diagnostic Methods
Giant cell bone tumors usually present with the following symptoms:
- Bone pain
- Swelling
- Tenderness
These tumors are usually found in the long bones, especially the knee bone and the upper arm bone. Diagnostic methods include:
- X-ray: Used to examine abnormalities in bone structure.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Determines the size and extent of spread of the tumor.
- Computed Tomography (CT): Provides detailed imaging.
- Biopsy: Performed to determine the characteristic features of the tumor.
5. Treatment Approaches
Surgery is usually the primary choice in the treatment of giant cell bone tumors. Treatment methods may include:
- Surgical Intervention: The goal is to remove the tumor.
- Bone-Sparing Surgery: Bone grafts are used to remove the tumor.
- Endoprosthetic Surgery: Artificial joint prostheses are used.
6. Surgical Treatment
Surgical treatment for giant cell bone tumors usually involves removing the tumor. Surgical procedures vary depending on:
- Size of the tumor: Surgery may be more complicated for larger tumors.
- Location of the tumor: Different techniques may be applied to preserve the limbs.
- Degree of spread: The condition of the tissues surrounding the tumor affects the surgery.
7. Conclusions and Future Directions
After the treatment process for giant cell bone tumors, surgical treatment usually yields effective results. However, the risk of recurrence and distant metastasis may continue after a certain period of time. Future directions include:
- Immunotherapy: Treatment approaches targeting the immune system.
- Genetic Profiling: Personalized treatment strategies.
- Multidisciplinary Approaches: Improved follow-up processes after treatment.
These approaches may provide more effective and targeted control of the disease.










