Bone Marrow Cancer: Definition, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Introduction
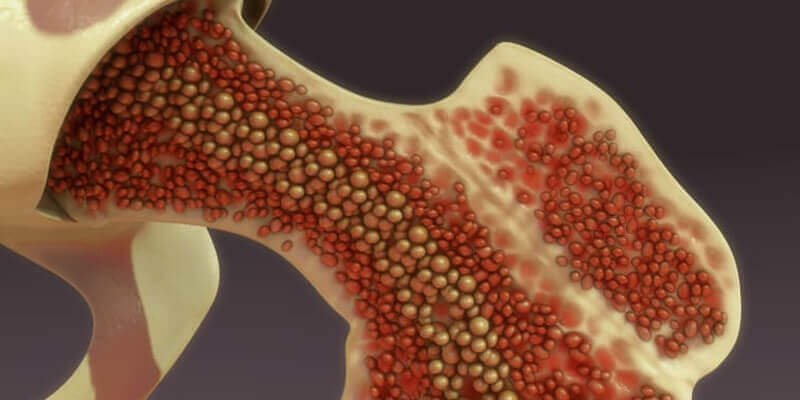
Bone marrow cancer is a disease that occurs when cancerous cells multiply uncontrollably in the bone marrow. This condition, which prevents the production of normal blood cells, can lead to various health problems. In this article, you can find detailed information about bone marrow cancer.
What is Bone Marrow Cancer?
Bone marrow cancer is a type of cancer that develops in the tissues that produce blood cells in the inner part of large bones. The uncontrolled proliferation of cancerous cells affects the production of healthy blood cells and can cause serious problems in the body. Bone marrow cancer is considered a different category from other types of cancer.
Types of Bone Marrow Cancer
Bone marrow cancer is seen in various types. The most common types are:
- Plasma Cell Cancer: It occurs as a result of uncontrolled growth of plasma cells.
- Lymphocytic Leukemia: It develops as a result of cancerous growth of cells called lymphocytes.
- Myeloid Leukemia and Lymphoma: It is among the other types.
The symptoms and treatment methods of each type may differ.
Symptoms and Signs
Common symptoms of bone marrow cancer are:
- Weakness and anemia
- Bone pain
- Susceptibility to infections
- Easy bruising
- Weight loss and loss of appetite
- Fever and sweating
It is important for people experiencing these symptoms to consult an oncologist for early diagnosis.
Diagnostic Methods
Methods used in the diagnosis of bone marrow cancer are as follows:
- Blood Tests: Complete blood count and biochemistry tests are used to investigate the presence of cancer cells.
- Bone Marrow Biopsy: The type of cancer is determined by samples taken from the bone marrow.
- Imaging Tests: X-ray, MRI and CT scans examine the spread of cancer.
- Genetic Tests: Analyzes the genetic structure of the cancer and clarifies treatment options.
Treatment Options
Methods used in the treatment of bone marrow cancer are as follows:
- Chemotherapy: Drugs are used to kill cancer cells.
- Radiotherapy: Cancer cells are targeted with high-energy rays.
- Bone Marrow Transplant: Healthy marrow is transplanted instead of damaged bone marrow.
- Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy: New methods are making progress in cancer treatment.
A specialist healthcare team should be consulted to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
Prognosis and Follow-up
The prognosis of bone marrow cancer depends on the stage of diagnosis, the type of cancer, and the patient's general health. Post-treatment follow-up includes regular check-ups to prevent recurrence of the disease and detect complications early. The patient's condition is monitored with blood tests, imaging methods, and physical examinations.










