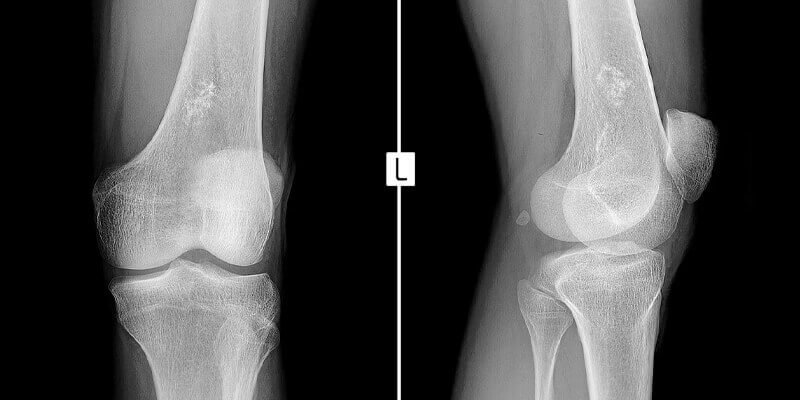
Ewing Sarcoma: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Research
Introduction
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of Ewing Sarcoma. The definition of the disease, treatment methods, recent developments, and research will be discussed. In addition, topics such as etiology, pathophysiology, epidemiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic methods, treatment options, and prognosis will be examined in detail.
What is Ewing Sarcoma?
Ewing Sarcoma is a rare type of cancer that usually occurs in the bones and rarely in soft tissues. It is more common in children and young adults and is usually found in the long bones. This tumor is associated with genetic changes, especially translocations on chromosomes 11 and 22.
Etiology and Pathophysiology
Although the exact causes of Ewing Sarcoma are not fully known, it is thought to occur as a result of the interaction of genetic and environmental factors. Genetic changes on chromosomes 11 and 22 play an important role in the formation of the disease. Environmental factors such as radiation can also be considered among the risk factors.
Epidemiology
This disease is usually seen between the ages of 10-20 and is slightly more common in males. The majority of cases are in white individuals, while it is rarely seen in other races.
Clinical Findings and Diagnostic Methods
Clinical symptoms in Ewing Sarcoma cases may vary from patient to patient. Diagnosis is usually made by a combination of methods.
Signs and Symptoms
- Pain and swelling
- Bone fractures
- Fever
- Weight loss
- Fatigue and loss of appetite
Imaging Methods
- X-ray
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Computed Tomography (CT)
- PET scans
- Bone scintigraphy
Biopsy and Pathologic Evaluation
Biopsy is critical for definitive diagnosis. The tissue samples taken are examined pathologically and the characteristics, cell type and staging of the tumor are determined.
Treatment Approaches
Methods such as surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy and targeted therapies are used in the treatment of Ewing Sarcoma.
Surgical Treatment
Surgical interventions can be performed to remove the tumor. Treatment is supported with chemotherapy and radiotherapy after surgery.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is an effective method used to shrink the tumor and prevent metastasis. It is applied with a multidisciplinary approach.
Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy is applied for local tumor control and symptom relief. Modern techniques cause minimal damage to surrounding tissues.
Targeted Therapies
Molecular targeted drugs and immunotherapies are applied with the principle of minimal damage to healthy tissues. These treatment methods may find wider use in the future.
Prognosis and Follow-up
Regular follow-up after treatment is critical to improving the quality of life of patients and reducing the risk of recurrence.
Risk Factors
- Tumor size
- Localization
- State of surgical margins
- Genetic characteristics
Recurrence and Metastasis
Recurrence and metastasis are important factors that determine the course of the disease. Regular follow-up and early diagnosis play an important role in reducing these risks.
New Treatment Developments and Research
New methods and research in the treatment of Ewing Sarcoma are promising for patients.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy, which aims to fight the tumor by strengthening the immune system, has shown significant developments in recent years.
Development of Targeted Therapies
Molecular targeted treatments offer more effective treatment plans when combined with genetic profiling.
Conclusion and Recommendations
A multidisciplinary approach should be adopted in the treatment of Ewing Sarcoma and support should be given to research aimed at improving the quality of life of patients. It is of great importance to develop more effective treatment methods and support clinical studies in this field.










